The Backbone of Global Commerce: An Insight into Modern Logistics
페이지 정보

본문
In today's fast-paced, interconnected world, logistics serves as the lifeblood of global commerce. Without effective logistics systems, the flow of goods and services would grind to a halt, paralyzing economies and halting supply chains. Whether it's the movement of raw materials to factories or the delivery of finished products to consumers, logistics ensures that goods are transported efficiently, on time, and within budget. Let’s dive into the essentials of logistics and explore how it shapes industries, economies, and daily life.
The Basics of Logistics
Logistics, at its core, is the process of planning, implementing, and managing the movement and storage of goods from point A to point B. This could involve anything from transporting goods across international borders to ensuring that food arrives fresh at local supermarkets. It includes several key activities such as warehousing, inventory management, transportation, and order fulfillment. By streamlining these processes, businesses can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
The Evolution of Logistics
The history of logistics stretches back to ancient times when early civilizations transported goods via caravans, rivers, and sea routes. However, logistics as we know it today began to take shape during the industrial revolution when railroads and steamships revolutionized long-distance transportation. In the modern era, the rise of e-commerce, globalization, and technological advancements like automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have dramatically transformed the field.
Today’s logistics networks are incredibly complex, involving multiple modes of transport—land, air, and sea— and covering vast distances across continents. As global trade continues to expand, logistics has evolved to include sophisticated tracking systems, real-time data monitoring, and agile supply chain management practices.
Key Components of Logistics
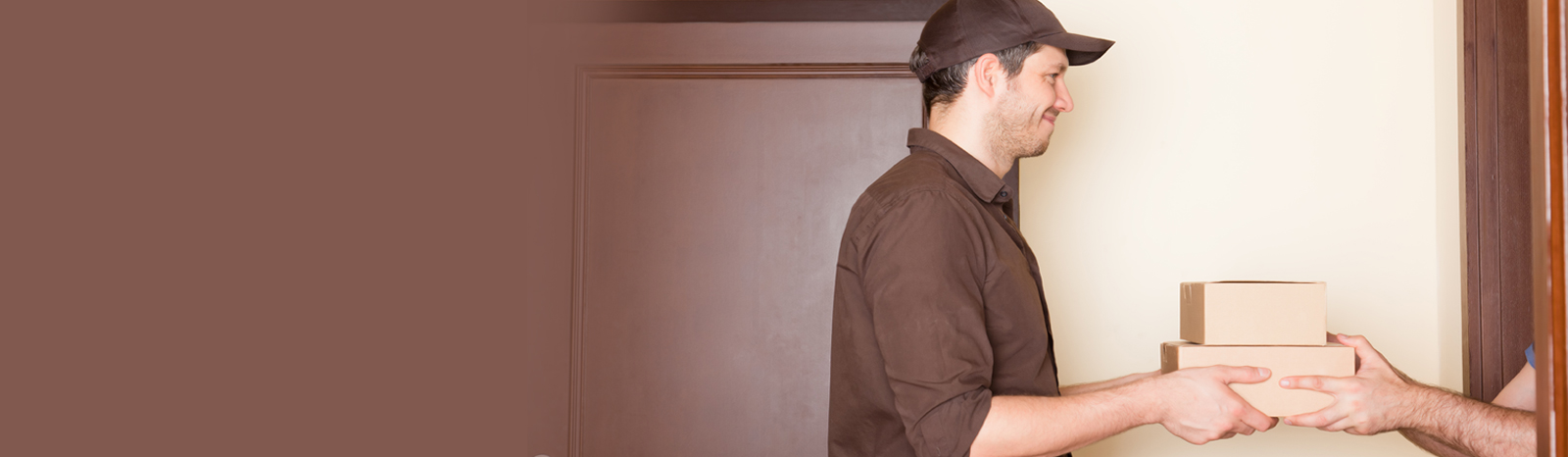 1. Transportation: One of the most visible aspects of logistics is the movement of goods. This includes trucking, shipping, rail, and air transport. Each mode comes with its advantages and challenges—trucks are flexible and can go almost anywhere, but ships are more cost-effective for bulk cargo over long distances.
1. Transportation: One of the most visible aspects of logistics is the movement of goods. This includes trucking, shipping, rail, and air transport. Each mode comes with its advantages and challenges—trucks are flexible and can go almost anywhere, but ships are more cost-effective for bulk cargo over long distances.
2. Warehousing: Storing goods safely before they’re shipped to their destination is another crucial component. Efficient warehousing minimizes delays, protects inventory, and ensures quick access to products when needed. Modern warehouses are increasingly automated, with robots and AI-driven systems enhancing storage efficiency.
3. Inventory Management: Managing inventory levels to meet customer demand without overstocking is key to reducing waste and controlling costs. This involves precise forecasting and tracking systems to maintain the right balance of stock.
4. Order Fulfillment: This stage ensures that customer orders are processed, packed, and shipped in a timely manner. With the rise of e-commerce, customers expect fast delivery, making this a vital part of the logistics chain.
The Role of Technology
Technology has revolutionized logistics, introducing innovations that boost efficiency, accuracy, and transparency. For example, GPS systems allow for real-time tracking of shipments, giving companies and customers visibility into the status of their goods. AI-powered algorithms optimize routes for transport, reducing fuel costs and delivery times. Additionally, drones and autonomous vehicles are being tested for last-mile deliveries, hinting at the future of logistics.
Blockchain is another technology poised to reshape logistics by providing a secure, transparent ledger for transactions, reducing fraud and errors in supply chain management.
Challenges Facing Modern Logistics
Despite these advancements, the logistics industry faces several challenges. Rising fuel costs, environmental concerns, labor shortages, and global disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic have exposed vulnerabilities in supply chains. Companies must constantly adapt, seeking out new technologies and sustainable practices to stay competitive in a rapidly changing landscape.
Conclusion
Logistics is much more than just moving goods from one place to another—it’s the intricate system that keeps economies running. As the world becomes increasingly globalized and digital, the demand for more efficient, faster, and sustainable logistics solutions will only grow. The future of logistics lies in embracing innovation and ensuring flexibility to meet the evolving demands of a connected world.
The Basics of Logistics
Logistics, at its core, is the process of planning, implementing, and managing the movement and storage of goods from point A to point B. This could involve anything from transporting goods across international borders to ensuring that food arrives fresh at local supermarkets. It includes several key activities such as warehousing, inventory management, transportation, and order fulfillment. By streamlining these processes, businesses can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve customer satisfaction.
The Evolution of Logistics
The history of logistics stretches back to ancient times when early civilizations transported goods via caravans, rivers, and sea routes. However, logistics as we know it today began to take shape during the industrial revolution when railroads and steamships revolutionized long-distance transportation. In the modern era, the rise of e-commerce, globalization, and technological advancements like automation and artificial intelligence (AI) have dramatically transformed the field.
Today’s logistics networks are incredibly complex, involving multiple modes of transport—land, air, and sea— and covering vast distances across continents. As global trade continues to expand, logistics has evolved to include sophisticated tracking systems, real-time data monitoring, and agile supply chain management practices.
Key Components of Logistics
 1. Transportation: One of the most visible aspects of logistics is the movement of goods. This includes trucking, shipping, rail, and air transport. Each mode comes with its advantages and challenges—trucks are flexible and can go almost anywhere, but ships are more cost-effective for bulk cargo over long distances.
1. Transportation: One of the most visible aspects of logistics is the movement of goods. This includes trucking, shipping, rail, and air transport. Each mode comes with its advantages and challenges—trucks are flexible and can go almost anywhere, but ships are more cost-effective for bulk cargo over long distances.2. Warehousing: Storing goods safely before they’re shipped to their destination is another crucial component. Efficient warehousing minimizes delays, protects inventory, and ensures quick access to products when needed. Modern warehouses are increasingly automated, with robots and AI-driven systems enhancing storage efficiency.
3. Inventory Management: Managing inventory levels to meet customer demand without overstocking is key to reducing waste and controlling costs. This involves precise forecasting and tracking systems to maintain the right balance of stock.
4. Order Fulfillment: This stage ensures that customer orders are processed, packed, and shipped in a timely manner. With the rise of e-commerce, customers expect fast delivery, making this a vital part of the logistics chain.
The Role of Technology
Technology has revolutionized logistics, introducing innovations that boost efficiency, accuracy, and transparency. For example, GPS systems allow for real-time tracking of shipments, giving companies and customers visibility into the status of their goods. AI-powered algorithms optimize routes for transport, reducing fuel costs and delivery times. Additionally, drones and autonomous vehicles are being tested for last-mile deliveries, hinting at the future of logistics.
Blockchain is another technology poised to reshape logistics by providing a secure, transparent ledger for transactions, reducing fraud and errors in supply chain management.
Challenges Facing Modern Logistics
Despite these advancements, the logistics industry faces several challenges. Rising fuel costs, environmental concerns, labor shortages, and global disruptions like the COVID-19 pandemic have exposed vulnerabilities in supply chains. Companies must constantly adapt, seeking out new technologies and sustainable practices to stay competitive in a rapidly changing landscape.
Conclusion
Logistics is much more than just moving goods from one place to another—it’s the intricate system that keeps economies running. As the world becomes increasingly globalized and digital, the demand for more efficient, faster, and sustainable logistics solutions will only grow. The future of logistics lies in embracing innovation and ensuring flexibility to meet the evolving demands of a connected world.
- 이전글Engaging Social Media Campaign Ideas for 2024 for Beginners 24.09.14
- 다음글What Will Costa Syrups Be Like In 100 Years? 24.09.14
댓글목록
등록된 댓글이 없습니다.